Oral cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its severity, early detection and awareness can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. In this article, we will discuss oral cancer, its symptoms, risk factors, and the importance of regular screening.
Understanding Oral Cancer
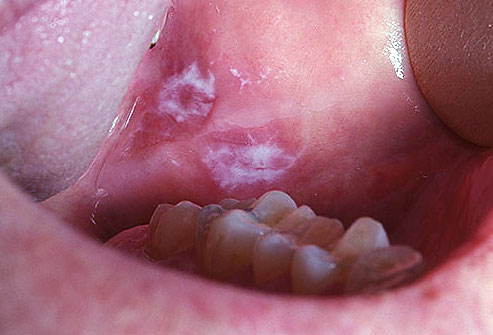
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the oral cavity, which includes the lips, tongue, gums, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth (palate), and the floor of the mouth. This type of cancer can be particularly aggressive if not detected and treated in its early stages.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer can manifest through various symptoms, which may include:
1. Persistent Mouth Sores: Ulcers, white or red patches, or sores that do not heal within two weeks should be cause for concern.
2. Pain or Discomfort: Ongoing pain, tenderness, or numbness in the mouth, throat, or face should be investigated.
3. Difficulty Swallowing: If you experience difficulty swallowing, it could be due to a tumor obstructing the throat or esophagus.
4. Changes in Voice: Hoarseness, persistent voice changes, or a sore throat that does not improve should not be ignored.
5. Lump or Mass: A lump, thickening, or swelling in the mouth or neck area could be a sign of oral cancer.
6. Unexplained Bleeding: Unexplained bleeding in the mouth, such as bleeding gums or blood in saliva, requires attention.
7. Dramatic Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can be a symptom of advanced oral cancer.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing oral cancer, including:
1. Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using smokeless tobacco significantly increases the risk of oral cancer.
2. Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption, especially when combined with tobacco use, raises the risk.
3. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, are linked to an increased risk of oral cancer.
4. Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight without lip protection can increase the risk of lip cancer.
5. Age: Oral cancer is more common in older adults, with the risk increasing after age 45.
6. Gender: Men are at a higher risk of developing oral cancer than women.
7. Poor Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of oral cancer.
Oral cancer awareness, early detection, and risk factor management are crucial for preventing the progression of this disease. Regular dental check-ups and open communication with your dentist can help ensure timely screening and, if needed, prompt intervention. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and the importance of screenings, you can take proactive steps towards protecting your oral health and overall well-being. If you notice any concerning symptoms, do not hesitate to seek professional evaluation and guidance.
Designed By Infinite Digital