Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet often underestimated dental condition that can have serious consequences for your oral health. In this article, we will explore the signs, treatment options, and prevention strategies for gum disease to help you maintain healthy gums and teeth throughout your life.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on your teeth and along the gumline. If not effectively removed through proper oral hygiene practices, plaque can harden into tartar, which leads to the development of gum disease.
Signs and Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease progresses in stages, with mild symptoms in its early stages and more severe symptoms as it advances:
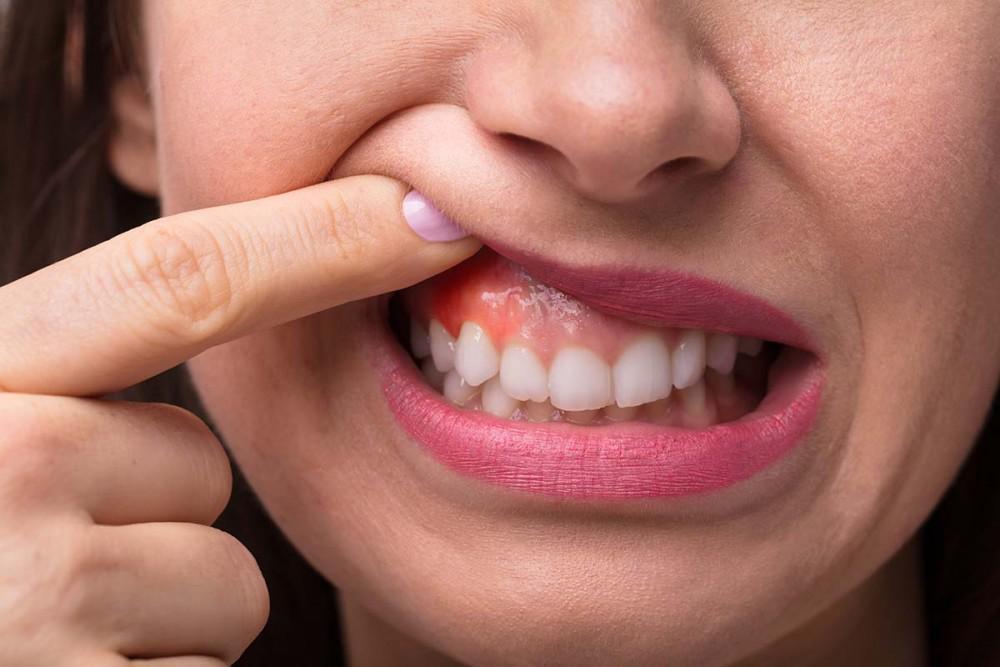
1. Gingivitis : This is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by:
– Red, swollen, and tender gums
– Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing
– Bad breath (halitosis) Gingivitis is usually reversible with improved oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings.
2. Periodontitis : If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. Symptoms include:
– Persistent bad breath
– Receding gums, exposing the tooth roots
– Formation of pockets between teeth and gums
– Loose or shifting teeth
– Changes in your bite Periodontitis can lead to irreversible damage to the supporting structures of your teeth.
Treatment for Gum Disease
The treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Scaling and Root Planing : In the early stages of gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be performed. This involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smoothing the tooth roots to encourage gum reattachment.
2. Surgical Procedures : Advanced cases of gum disease may require surgical intervention. Procedures like flap surgery and bone grafts can help repair damaged tissues and restore gum health.
3. Antibiotics : In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection and reduce inflammation.
4. Maintenance : Following treatment, regular dental checkups and cleanings are essential to monitor your gum health and prevent a recurrence of gum disease.
Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is key when it comes to gum disease. Here’s how you can protect your gums and oral health:
1. Proper Oral Hygiene : Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent its buildup.
2. Regular Dental Checkups : Visit your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings. Your dentist can detect gum disease in its early stages and provide guidance on proper oral care.
3. Quit Smoking : Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce your risk.
4. Healthy Diet : A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low in sugary and acidic foods can promote gum health.
5. Manage Stress : Chronic stress can weaken your immune system and increase the risk of gum disease. Practice stress-reduction techniques.
Gum disease is a common yet preventable condition that can lead to serious oral health issues if left untreated. By recognizing the signs, seeking timely treatment, and adopting good oral hygiene practices, you can protect your gums and maintain a healthy smile. Regular dental checkups are crucial in catching gum disease early and ensuring that your oral health remains in optimal condition.
Designed By Infinite Digital